Microsoft has encompassed its own antimalware program in Windows named Windows Defender. It can also protect you from ransomware with Controlled Folder Access. Windows Defender works very well as long as you follow all best practices about using a computer and interacting with the Internet carefully.
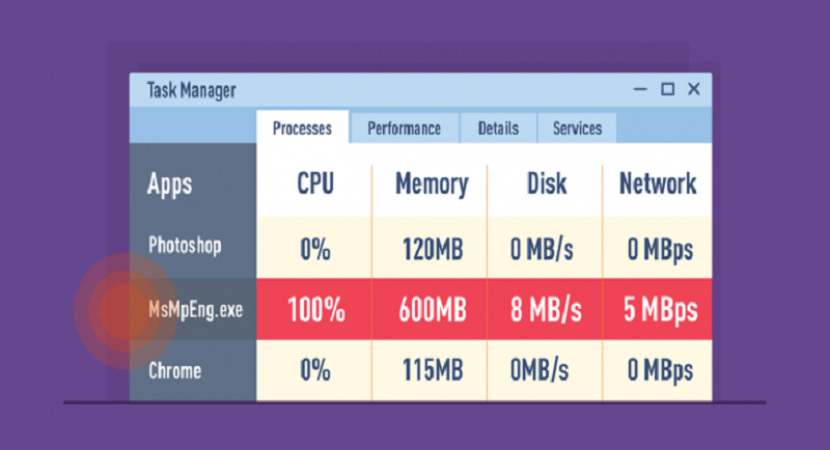
However, sometimes Windows Defender’s CPU usage can be very high, anywhere between 30-90%. When you open Task Manager, Windows Defender’s actual CPU usage is displayed next to the “Antimalware Service Executable.” The process Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, is related to Windows Defender Protection Module. Due to a number of reasons such as system crashes, malware infections, etc., the antimalware service executable file can consume a large number of CPU resources which slow down the normal operation of your system.
If you are facing this problem, we will show you how to Fix Antimalware Service Executable high CPU usage in Windows 10.
Solution 1 – Check for the Viruses
First and foremost, the thing you should do to fix Windows Defender’s high CPU usage indicates whether your system is infected with the virus, malware, or adware. This is because your system may be infected and Windows Defender is actively trying to remove the infection from the system, which in turn results in high CPU usage.
- If you haven’t installed a third-party antivirus program then, you can scan the system with Windows Defender.
- We need to do a deep scan or a full scan. In the Threat Prevention window, click the “Run a new advanced scan” link that appears under the “Scan now” button.
- Now hit the “Full Scan” option and select the “Scan Now” option.
It may take a few hours to complete the scan. If any virus or threat is found then, it would be removed automatically.
Also, we recommend that you scan your system with any other reliable antimalware program.Now if your system doesn’t have any malware or viruses and the problem remains the same, then try the next solution.
Solution 2 – Dismiss Windows Defender
Windows Defender continuously runs in the background and regularly monitors your system for threats like viruses, malware, and trojans. While it scans various system processes. This is commonly known as real-time protection.
Since Windows Defender monitors all processes, it relates to the scanning process. This can sometimes lead to a loop-like situation, trying to scan yourself for unfamiliar activities. This is a cause of the high CPU usage by Antimalware Service Executable. You can add Windows Defender to Windows Defender Exclusion List yourself to avoid high CPU usage by Antimalware Service Executable.
Once you’ve added Windows Defender to the exclusion list, it doesn’t keep checking itself, which in turn reduces Windows Defender’s high CPU usage.
This method might work for most Windows users. So, there are chances that it would work for you as well.
- First, look for “Windows Defender Settings” in the start menu and open it.
- In the Windows Security window, click the Virus and threat protection option in the Protection Areas section that appears in the right pane.
- In this window, select Virus & Threat Protection Settings, scroll to the bottom, and click the Add or Remove Exclusions link in the Exclusions section.
- From here you can add any folder, file, file type, or process to the Windows Defender exclusion list. Click the Add Exclusion button and select the Folder option.
- In the C: ProgramDataMicrosoftSelect Folder window, go to Select the Windows Defender folder, and then click the Select Folder button to add the Windows Defender folder to the exclusion list.
Note: You may get a User Access Control (UAC) prompt. Simply click the “Yes” button to continue.
That’s it. You have successfully excluded Windows Defender and stopped it from regularly scanning. Reboot your system and you would no longer experience high CPU usage for the Antimalware Service Executable process.
If you continue to have an issue with the Antimalware Service Executable high CPU usage, you may also want to try the following methods.
Solution 3 – Turn Off Ream-Time Protection
If the aforementioned solutions didn’t work, then as a final method you can try disabling Windows Defender’s real-time protection. Since Antimalware Service Executable’s high CPU usage is caused by real-time protection, disabling it can resolve the issue immediately. Well, we would not recommend turning off real time protection for a very long time. You can try this solution to fix high CPU usage by Antimalware Service Executable temporarily. If you re-enable real-time protection, Windows Defender’s high CPU will experience many problems again.
- First, open Windows Defender by searching for “Windows Defender Security Center” in the Start menu. Go to Virus and Threat Protection and click the Virus and Threat Protection Settings option.
- In the right-hand area, switch the button under “Real-time protection” to “Off”. You will get a UAC (User Access Control) prompt. Click the Yes button to continue.
That’s all. Windows Defender disables real-time protection and there is no longer a problem with the high CPU usage of Antimalware Service Executable.Again, this is only a temporary solution.
Solution 4 – Try Any Other Trusted Anti-Virus Program
When you have tried all of the solutions mentioned above and none of them worked for you then, we suggest you install third-party antimalware software on your Windows PC. Once you have installed any trusted antimalware program, you can disable Windows Defender completely, and Antimalware Service Executable will not use high CPU on your PC.
There are many options on the internet that provide efficient protection to windows users and secure their system. Kaspersky, Norton, AVG, and there are many more popular anti-virus programs. This way, you will not only fix Antimalware Service Executable High CPU usage but can also protect the whole system from any threat.


Reply